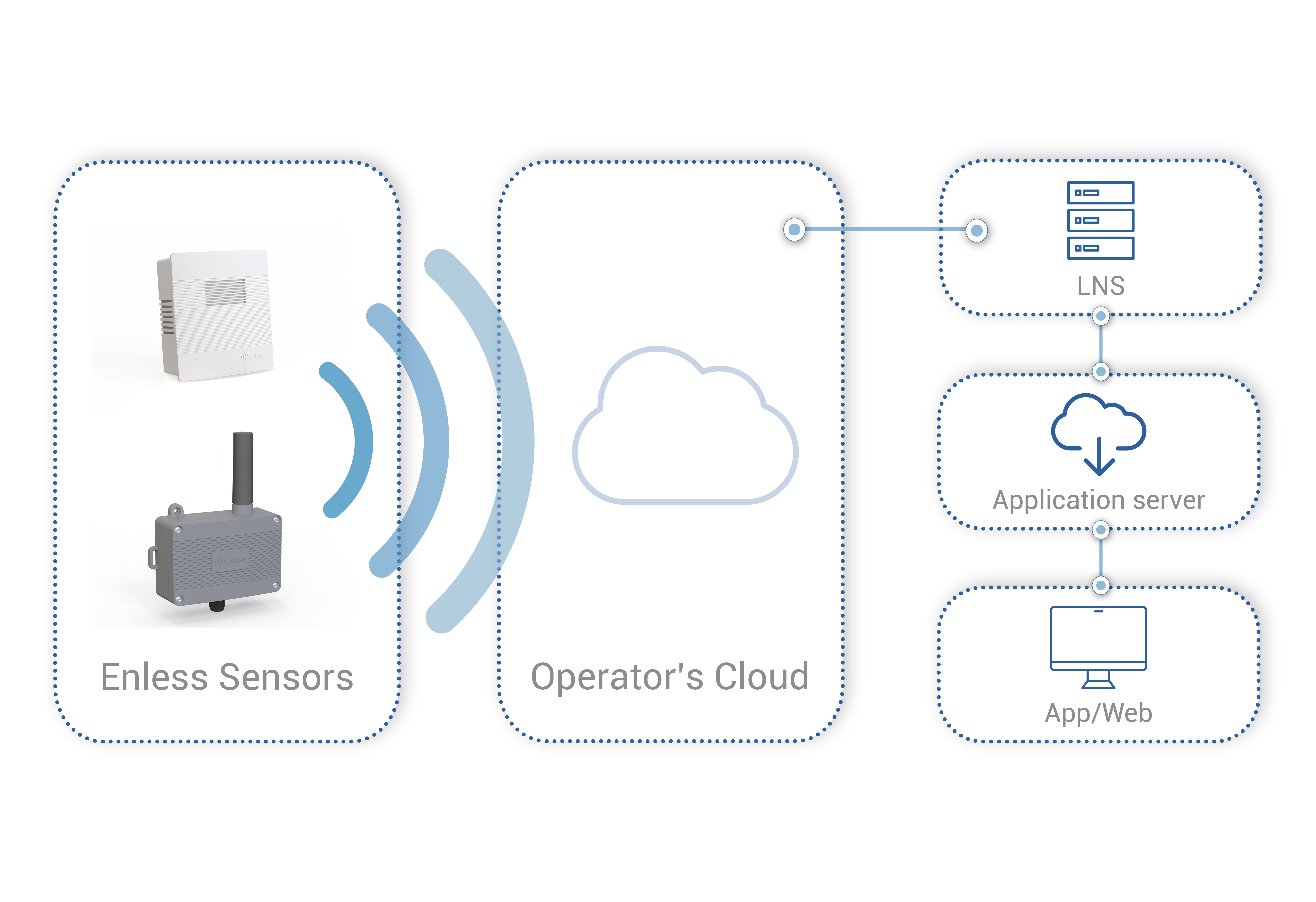
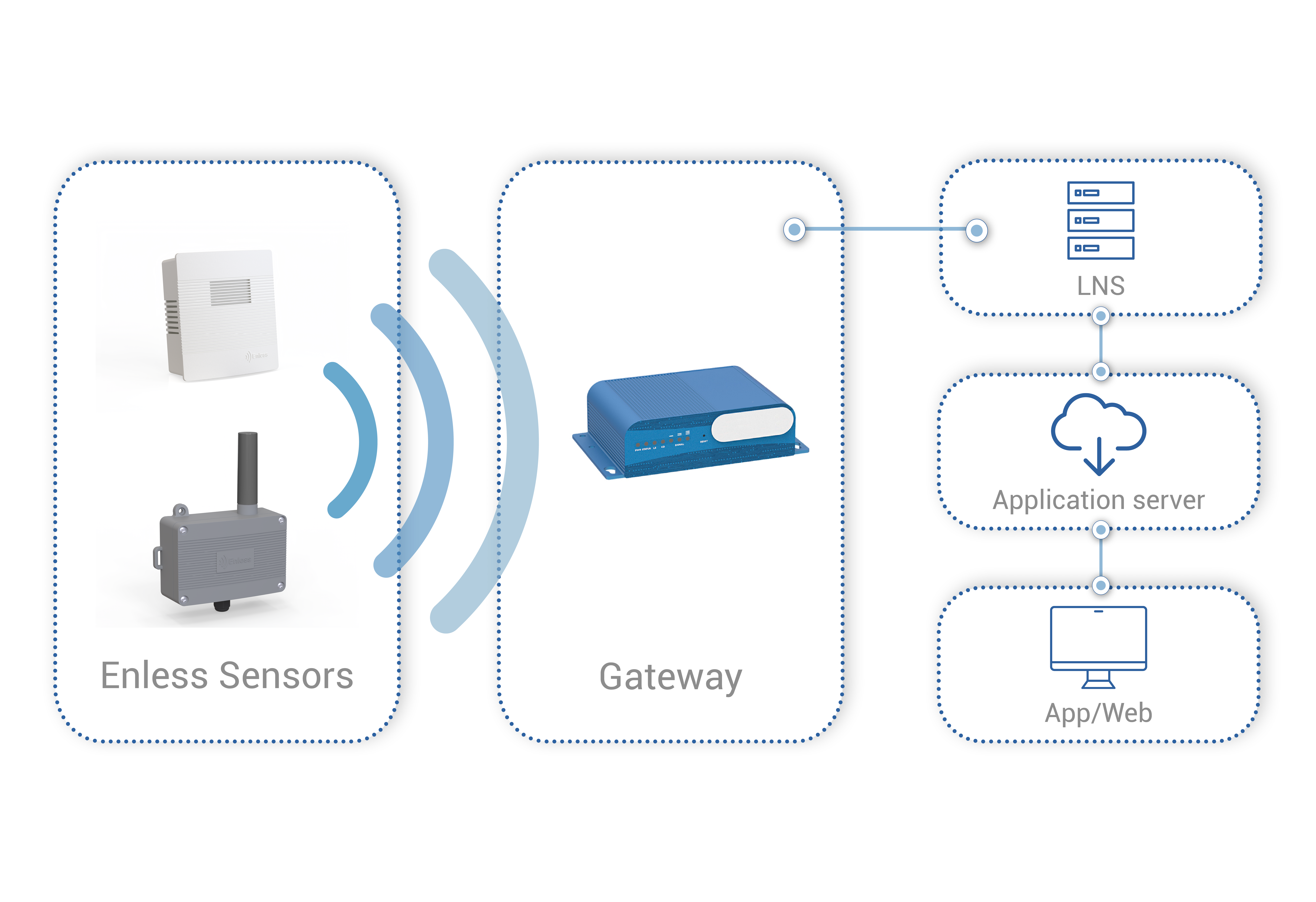
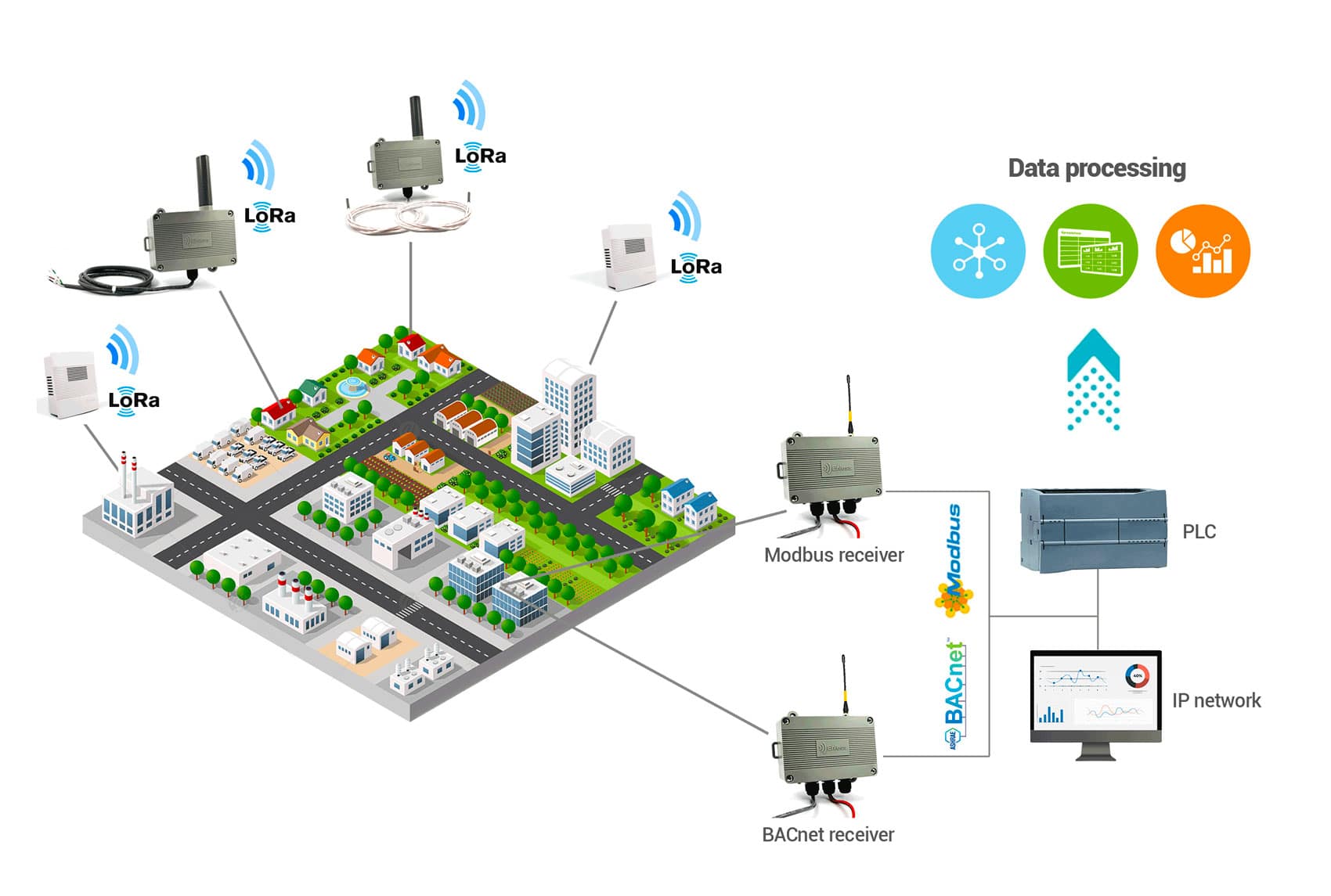
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly transforming industries by enabling smart devices to communicate over long distances with minimal power consumption. One of the technologies driving this revolution is LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network), a protocol designed for low-power, wide-area networks (LPWANs). However, LoRaWAN operates differently depending on the region, with EU868 and US915 being the primary frequency bands in Europe and North America, respectively. Understanding the differences between LoRaWAN EU868 and LoRaWAN US915 is crucial for developers and businesses looking to deploy IoT solutions.

What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a network protocol built on top of LoRa (Long Range) modulation, allowing for secure, bidirectional communication between IoT devices and central servers. It’s particularly suited for applications where devices need to transmit small amounts of data over long distances, such as smart meters, asset tracking, and environmental monitoring.
Frequency Bands: EU868 vs. US915
The most significant difference between LoRaWAN EU868 and LoRaWAN US915 lies in their frequency bands:
EU868:
Operates in the 863-870 MHz band, specifically allocated for unlicensed use in Europe. The exact frequencies used within this band can vary slightly between countries within the European Union, but the 868 MHz frequency is the most common.
US915:
Operates in the 902-928 MHz band, allocated for unlicensed use in the United States and much of North America. This band is slightly broader than EU868, allowing for more channels and higher data rates in some scenarios.
These frequency bands are determined by regional regulatory authorities and are crucial for ensuring that wireless devices do not interfere with each other or with other types of communication, such as cellular networks or emergency services.
Channel Plan and Bandwidth
One of the key technical differences between EU868 and US915 is their channel plans and bandwidth allocations:
EU868 Channel Plan:
-
- The EU868 band typically uses 8 channels.
- Each channel has a bandwidth of 125 kHz.
- There is an additional optional channel at 868.8 MHz with a 250 kHz bandwidth.
- The duty cycle is regulated, meaning that devices can only transmit a small percentage of the time to avoid congestion.
This is typically around 1%, depending on the sub-band.
US915 Channel Plan:
-
- The US915 band uses 64 channels, each with a 125 kHz bandwidth, and 8 additional channels with a 500 kHz bandwidth.
- The US915 plan allows for a higher number of simultaneous transmissions compared to EU868 due to the larger number of channels.
- Unlike EU868, US915 does not have strict duty cycle limitations, allowing for more frequent data transmission.
The difference in channel availability makes US915 more suitable for densely populated IoT deployments where many devices need to transmit data simultaneously. In contrast, EU868’s limited channels and strict duty cycle regulations make it better suited for scenarios with fewer devices or where power consumption needs to be minimized.
Transmission Power and Range
Transmission power is another area where these two bands differ:
EU868:
-
- The maximum transmission power is typically limited to 14 dBm (about 25 mW) in most European countries.
- This lower power level, combined with strict duty cycle regulations, can limit the range of LoRaWAN devices, especially in urban environments with significant interference or obstacles.
US915:
-
- The maximum transmission power allowed is up to 30 dBm (1 W) in the United States.
- The higher transmission power in US915 can result in a longer range, making it suitable for rural or remote deployments where devices need to communicate over several kilometers.
While the higher transmission power in US915 can extend the range of communication, it also increases power consumption, which may be a trade-off in battery-powered IoT devices.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Deploying LoRaWAN devices requires compliance with regional regulations:
EU868:
Devices must comply with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) regulations, specifically EN 300 220 for short-range devices and EN 301 489 for electromagnetic compatibility. Compliance with these standards is essential for legal operation in Europe.
US915:
Devices must adhere to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulations, specifically Part 15.247 for unlicensed radio frequency devices. FCC certification is mandatory for devices sold or deployed in the United States.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, legal action, or the need to recall and modify non-compliant devices.
Application Considerations
When deciding between LoRaWAN EU868 and US915 for your IoT deployment, consider the following factors:
Geographic Location:
The most obvious factor is the location of your deployment. EU868 is required for Europe, while US915 is necessary for North America. Deploying the wrong frequency band in the wrong region can lead to interference, regulatory issues, and poor network performance.
Device Density:
If your application involves a large number of devices in a confined area, US915’s larger number of channels may be beneficial. However, if power consumption is a concern, EU868’s lower transmission power and duty cycle limits could be more appropriate.
Range Requirements:
For applications requiring long-range communication, especially in rural areas, US915’s higher transmission power may provide the necessary range. In contrast, EU868 is better suited for shorter-range applications or environments with significant regulatory constraints.
Regulatory Compliance:
Always ensure that your devices are certified for the region in which they will be deployed. This includes adhering to local regulations for transmission power, duty cycle, and electromagnetic compatibility.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between LoRaWAN EU868 and LoRaWAN US915 is essential for successfully deploying IoT solutions. Each frequency band offers unique advantages and challenges, influenced by regional regulations, channel availability, and transmission power limits. By carefully considering your application’s requirements and the characteristics of each band, you can select the appropriate LoRaWAN frequency band to ensure reliable and compliant IoT communication.
Whether you’re planning a small-scale deployment in an urban environment or a large-scale network spanning rural areas, choosing the right LoRaWAN frequency band is a critical step toward achieving optimal performance and regulatory compliance.