LoRaWAN is a communication network founded by the LoRa Alliance, a non-profit association created in 2015 that initiated the LPWAN network (Low Power Wide Area Network). The LoRa Alliance has now become a benchmark in the technology sector and brings together many players who respond to IoT applications. The objective of this foundation is to allow wireless connectivity between IoT devices to a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN network) and to extend this standard internationally. According to a recent study by IoT Analytics, more than 660 million IoT devices were active on the LPWAN network in 2021.
There are several technologies on the market today that can connect to an LPWAN network (Sigfox, LoRaWAN, NB-IoT etc.) But then what is the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN?
How to use LoRaWAN technology?
LoRaWAN: what is it?
LoRaWAN is a communication protocol used on an LPWAN network, i.e. on a wide area but low power network. The LoRaWAN technology allows the transmission of small data over a long range for IoT devices such as sensors for example.
How to connect your IoT devices in LoRaWAN mode?
The communication links for IoT devices is done through LoRaWAN technology. There are 2 ways to use the LoRaWAN communication protocol:
The use of LoRaWAN technology in operated mode:
Several steps are essential to enable the wireless connectivity in operated mode:
- Use IoT devices compatible with LoRaWAN.
- Provision of a subscription with an operator that covers LoRaWAN technology.
See LoRaWAN coverage and the list of different operators. - Access to the operator’s Cloud (provided by the operator when purchasing subscriptions).
- Being able to view data stored in the operator’s cloud. If you are not directly equipped with a visualisation platform, it is possible to contact companies specially dedicated to the visualisation of IoT data.
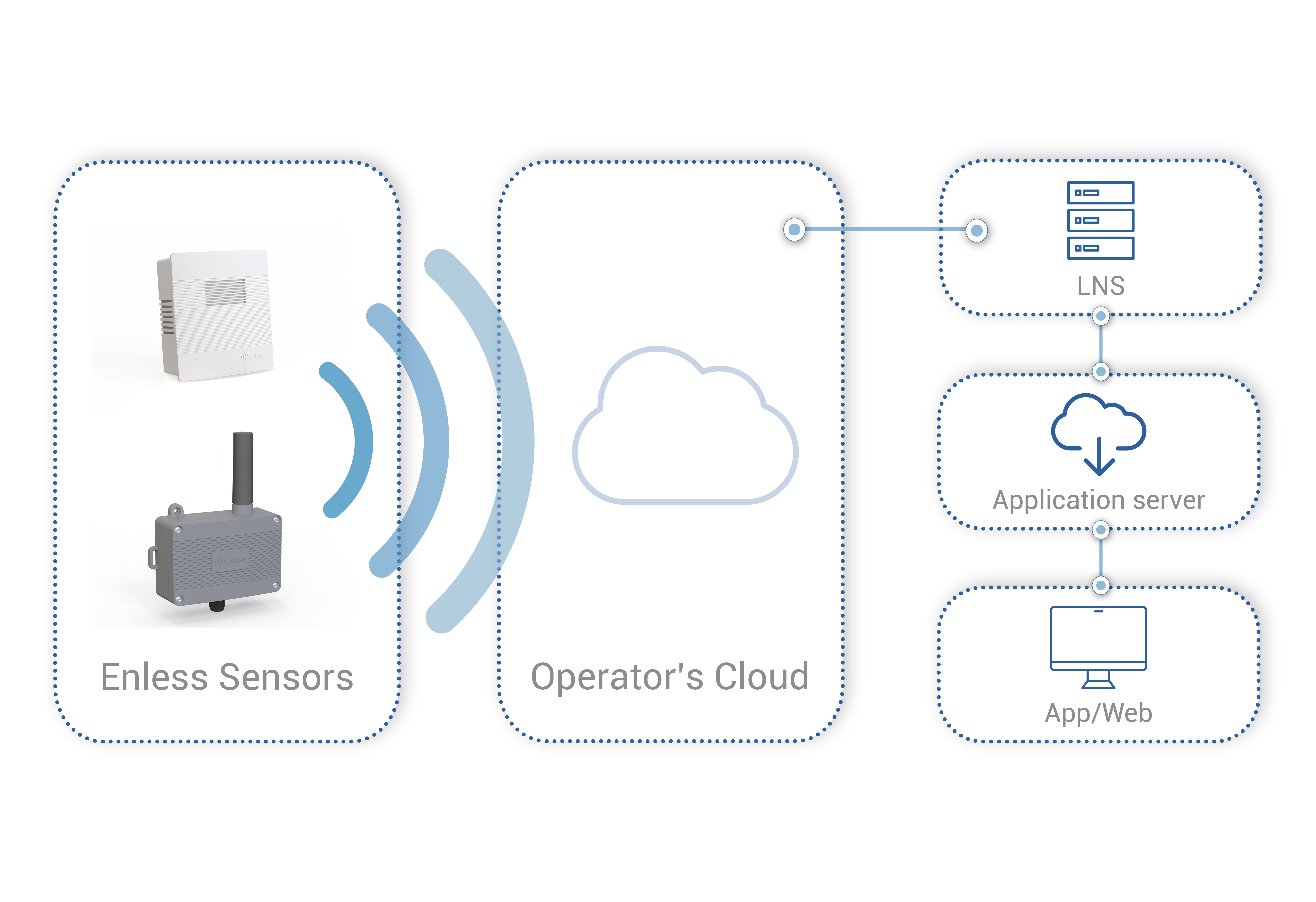
To better understand, here is an example of architecture in public mode with the LoRaWAN network:
In this example, Enless Wireless radio sensors were installed in a building to monitor indoor air quality. The wireless radio sensors are compatible with LoRaWAN technology and are used in operated mode.
Advantages:
- Low-cost subscription.
- Simple and quick to set up.
Disadvantages:
- Becomes expensive if you deploy a lot of devices on site (1 subscription for each device).
- Dependent on the operator networks which are not always present in rural areas or basements for example.
The use of LoRaWAN technology in private mode :
It is quite possible to use LoRaWAN technology without going through a public subscription with an operator. Indeed, the advantage of LoRaWAN is to allow you to build a private network. Here are the different steps to build a private network in LoRaWAN mode:
- Choose LoRaWAN compatible IoT devices.
- Have a LoRaWAN gateway available that will allow you to centralise all the data sent by your IoT devices.
- Have access to the LoRa Network Server (LNS) to store all the data of your IoT devices.
- You will need a data visualisation platform.
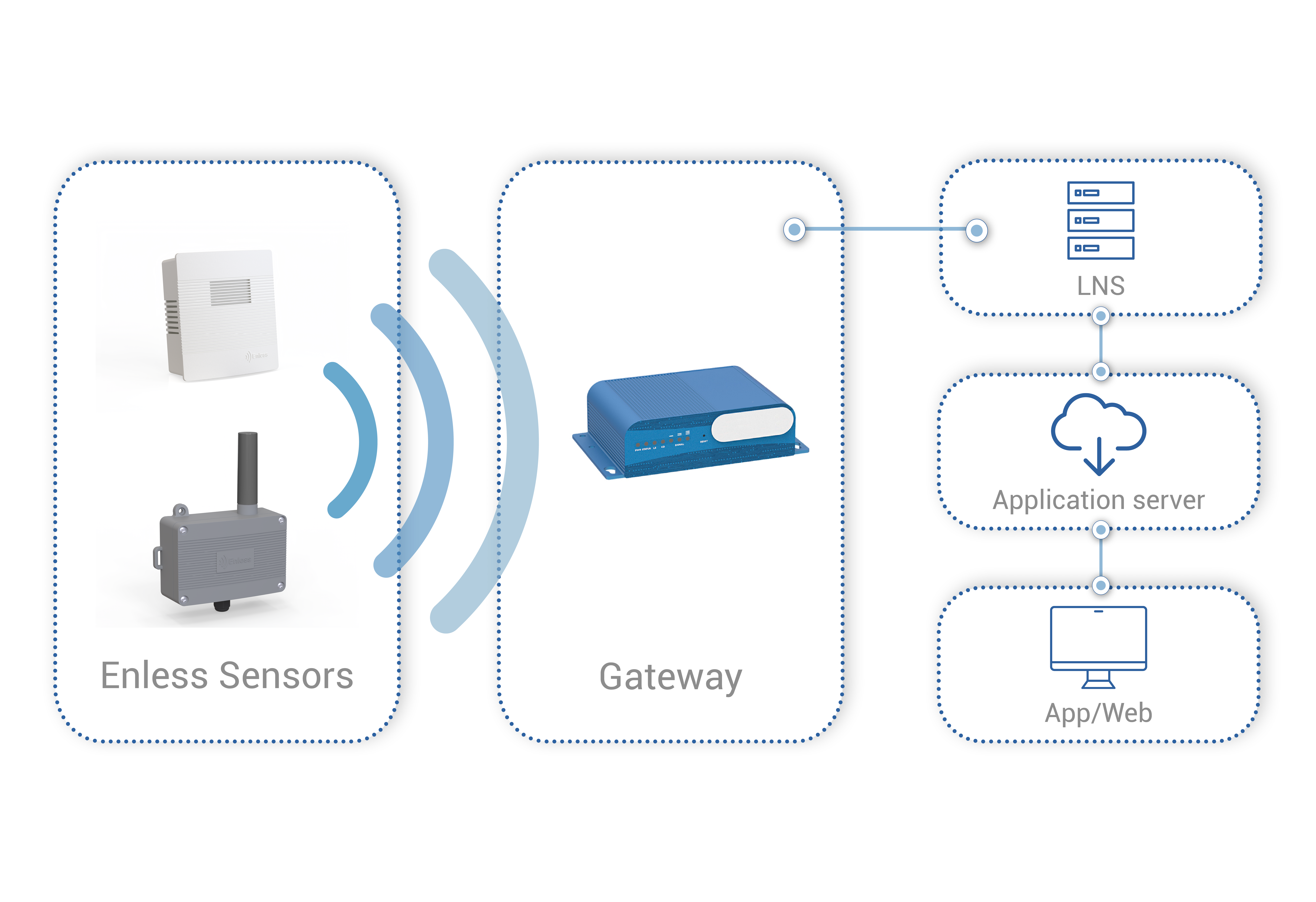
To better understand, here is an example of using LoRaWAN technology in a private network:
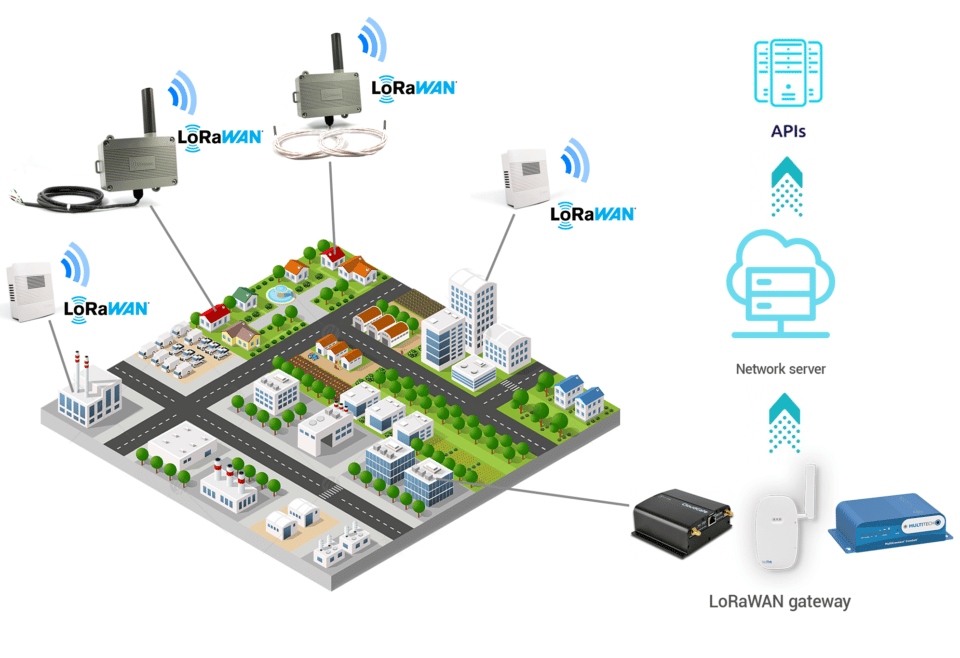
In this example, Enless Wireless radio sensors were installed to monitor indoor air quality. The radio sensors are compatible with LoRaWAN technology and are used in a private network.
Advantages:
- Allows deploying many devices on site.
- Allows building a private network without going through the public cloud.
Disadvantages:
- If you are not already equipped with a gateway, you will have to forecast and add the costs associated with this equipment.
- The device data goes through the cloud of the LoRa Network Server (NLS).
How to use LoRa technology?
LoRa: what is it?
LoRa technology is a private radio protocol. Unlike the LoRaWAN communication protocol, the data is not stored in a public cloud or the LoRa Network Server cloud. It is a technology that makes it possible to build a 100% private radio architecture. It will be necessary to use several radio devices and make them communicate with each other for data transmission. This is referred to as the Machine to Machine (MtoM) process.
How to connect your devices in LoRa mode?
Here are the different steps to build a private network in LoRa :
- Choose radio devices on LoRa technology.
- Equip yourself with a PLC on site to collect the information stored in the radio device.
- If you don’t have a PLC, you can use the building’s IP network.
- Have access to a data visualisation platform.
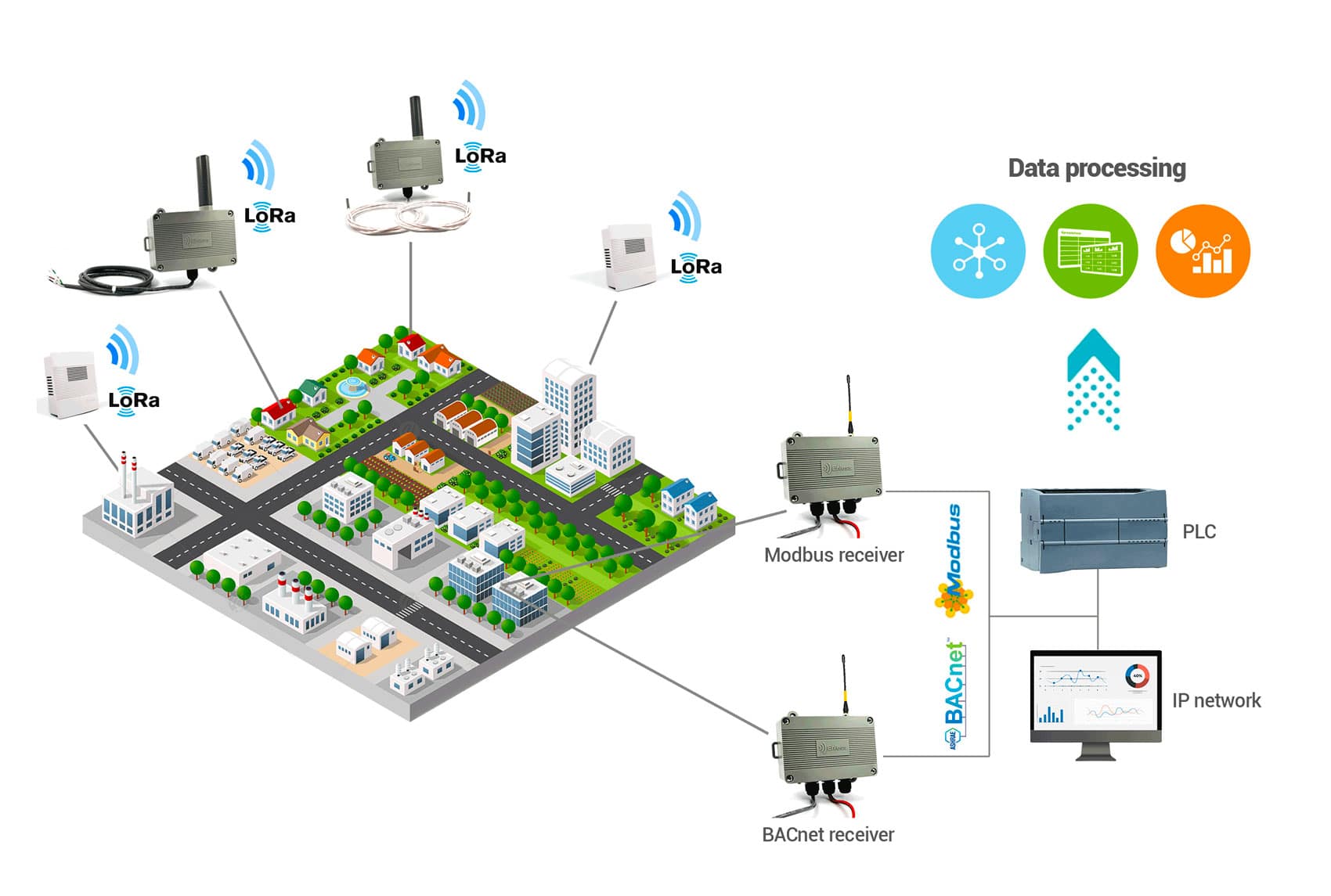
To better understand, here is an example of using LoRa technology in a private network:
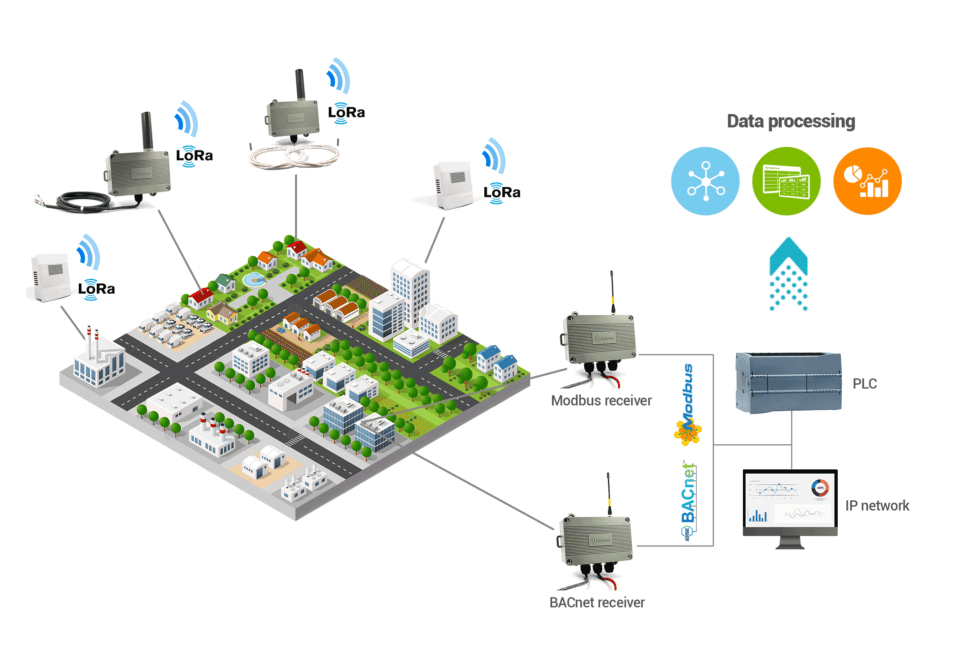
In this example, Enless Wireless radio sensors have been installed in a large area for several applications: remote meter reading, temperature measurement. Enless Wireless sensors send their data by radio to an Enless Wireless receiver (Machine to Machine process). The receiver stores the sensor data and is then connected either to a PLC or to the building’s IP network to collect the data.
How to choose between LoRaWAN and LoRa technologies?
In both cases, it is essential to have devices compatible with LoRaWAN / LoRa technologies. Depending on your needs, it will be preferable to choose one or the other means of radio communication. Here’s what to remember:
For LoRaWAN technology:

- Ability to switch between an operated network (public) or a private network. This will depend on the equipment you have available on site.
- As a whole, LoRaWAN allows you to view your device data easily and remotely.
- It allows data transmission on an extended and low-power network.
In summary, the choice to use LoRaWAN on a public network is an inexpensive solution suitable for a small deployment of IoT devices.
The use of LoRaWAN on a private network is advantageous when there is a large number of devices to be installed on a site and there is a need to centralise data.
For LoRa technology:

- It allows being independent of the coverage of the operator network.
- It eliminates the need to send data to a cloud.
- Allows remote control directly on site.
In summary, this solution is the most suitable if you do not want your data to transit to a cloud and you are deploying radio devices over a large area. It is also the best solution if you wish to carry out remote on-site regulation.